Call us
+919650935061Address
Nirman Nagar, JaipurGoogle Rating
5.0( 607+ Reviews )
Overview
What is Gum Surgery?

Overview
What is Gum Surgery?
Gum diseases are of different kinds, including Gingivitis, which happens to be a mild form of gum disease that affects the bone and tissue of and around your teeth. Periodontitis is, however, a much-advanced gum disease which can cause severely damaged bones and tissues and requires immediate dental operation. Gum surgery hospital in Jaipur removes these bacteria and restores the gums and teeth to their healthy state. Certain patients also undergo gum surgery as a cosmetic procedure to remove excessive gum above their teeth, causing a condition known as a ‘gummy smile’. There are different types of gum surgeries to treat this issue.
Signs That you Need
What are the Signs That you Need a Gum Surgery?
Understanding the signs of unhealthy gums is the first step to preventing any serious gum issues. Here are the signs you should never ignore:
Red and Swollen Gums
If your gums appear red and swollen or bleed very easily, even while brushing or eating, it could be a sign of a gum issue. Consider visiting a dentist to identify the underlying issue and get treatment.
History of Gum Disease
Gum diseases are genetic illnesses that can be passed down in families. If you have family members with gum diseases and suspect you might have one, it is wise to get your gums checked regularly by a dentist.
Gum Recession
Through gum recession, if the roots of your teeth show more than usual, it means the gums are pulling away. This could also hurt when you have something warm. In case of these symptoms, consider getting a dental check-up.
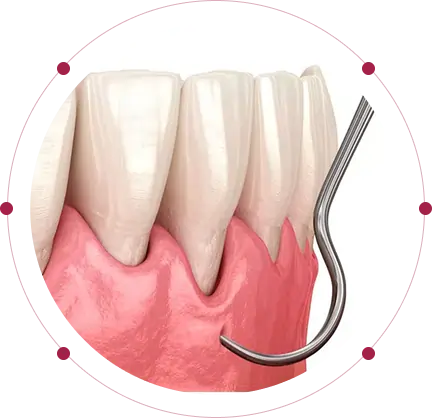
Bad Breath
While momentary bad breath is a common characteristic among many individuals, if you notice having bad breath at all times, even with proper oral care, it could mean something serious.
Sensitive Teeth
If your teeth are more sensitive than usual and are prone to getting cavities and tooth decay, it could point towards gum disease. This can be confirmed by seeing a dentist as soon as possible.
Weak Mobile Teeth
If you notice your teeth becoming mobile, it could be a sign of decreasing supporting tissues. In such a case, the teeth may also fall out or become extremely sensitive. It is essential to see a dentist to avoid tooth loss.

Red and Swollen Gums
If your gums appear red and swollen or bleed very easily, even while brushing or eating, it could be a sign of a gum issue. Consider visiting a dentist to identify the underlying issue and get treatment.
History of Gum Disease
Gum diseases are genetic illnesses that can be passed down in families. If you have family members with gum diseases and suspect you might have one, it is wise to get your gums checked regularly by a dentist.
Gum Recession
Through gum recession, if the roots of your teeth show more than usual, it means the gums are pulling away. This could also hurt when you have something warm. In case of these symptoms, consider getting a dental check-up.
Bad Breath
While momentary bad breath is a common characteristic among many individuals, if you notice having bad breath at all times, even with proper oral care, it could mean something serious.
Sensitive Teeth
If your teeth are more sensitive than usual and are prone to getting cavities and tooth decay, it could point towards gum disease. This can be confirmed by seeing a dentist as soon as possible.
Weak Mobile Teeth
If you notice your teeth becoming mobile, it could be a sign of decreasing supporting tissues. In such a case, the teeth may also fall out or become extremely sensitive. It is essential to see a dentist to avoid tooth loss.
Health Tips
Your Guide to a Healthier Smile
Our health tips video is given below which gives you a guide and practical advice to maintain a healthy smile. Learn expert tips from Dr. Renu on oral hygiene, preventive care, and nutrition to keep your teeth strong and bright every day.

15+ Years of Experience

Meet Our Doctor
Dr. Renu Chaudhary
BDS, MDS & PGCOI(PGI)
Dr. Renu Chaudhary has been performing in the dental field with over 15 years of experience and with more than 20,000 successful dental procedures. She offers various treatments for gum diseases, gum grafting and even cosmetic procedures to enhance smiles. With pain-free and affordable treatments available and the latest medical advancements, she is considered a top gum surgery specialist in Jaipur. Her services today are professional and done, ensuring the comfort and convenience of the patients.
20K+
Dental Procedures
10K+
Smile Makeovers
20K+
Happy Patients
Why Choose
Why Choose Dr. Renu Dental Clinic for Gum Surgery?
Dr. Renu Dental Clinic for gum surgery has remained renowned for its budget-friendly and successful gum surgeries in the past few years. Here is why you should choose this gum surgery clinic in Jaipur:
Years of Experience
Dr. Renu Chaudhary has decades of experience treating her patients. Her expertise lies in making patients comfortable and conducting successful procedures that are painless.
Advanced Clinic
Dr Renu Dental Clinic for Gum Surgery houses advanced equipment and medical innovations that minimise pain and maximise surgery success rates for patients.
Affordable Pricing
All the services available at the clinic remain affordable for the majority of people. The patients are offered cosmetic procedures, advanced tooth and gum solutions and infection-prevention surgeries, all at pocket-friendly prices.
Years of Experience
Dr. Renu Chaudhary has decades of experience treating her patients. Her expertise lies in making patients comfortable and conducting successful procedures that are painless.
Advanced Clinic
Dr Renu Dental Clinic for Gum Surgery houses advanced equipment and medical innovations that minimise pain and maximise surgery success rates for patients.
Affordable Pricing
All the services available at the clinic remain affordable for the majority of people. The patients are offered cosmetic procedures, advanced tooth and gum solutions and infection-prevention surgeries, all at pocket-friendly prices.
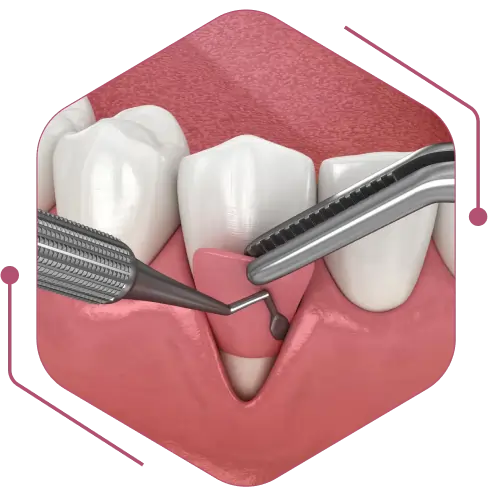
What are the Types of Gum Surgery?
Gum disease treatment in Jaipur has many forms, and some are done with advanced tools and technology, while others have been prevalent in dental procedures for a long. Here are the types:
- 1. Gingival Flap Surgery
In this gum surgery in Jaipur, the gums are temporarily separated from the teeth, and the dentist cleans the area to cleanse any bacterial debris. After that, the gums are stitched back to the teeth. Certain cases may also require bone reshaping afterward.
- 2. Gingivectomy
This particular surgery is meant to remove excess gum tissue that causes the phenomenon of gummy teeth. This is mostly done as a cosmetic procedure to enhance the appearance of people’s sets of teeth and to make it more convenient to keep oral hygiene in place.
- 3. Gingivoplasty
This is also a cosmetic procedure to enhance the smiles by reshaping the healthy gum tissue to form a suitable gum line. Usually, this procedure is done with a gum graft for a better result.
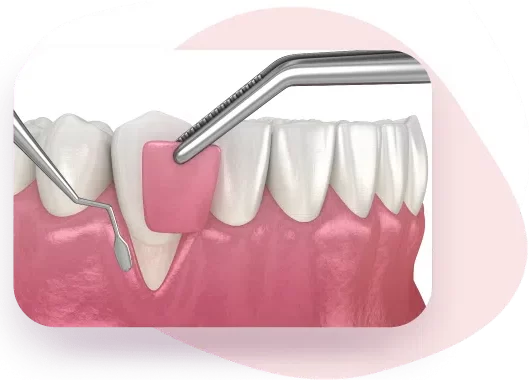
- 4. Gum Graft
In this gum surgery in Jaipur, healthy tissue is taken from the roof of the mouth, and the dentist stitches on either side of the tooth with receding gums. This process returns the gum line and also helps reduce teeth sensitivity in the area.
- 5. Gum Regeneration
This surgery is done to remove bacteria and promote gum tissue regeneration in the affected area. The dentist folds back the gum tissue and inserts membranes, grafts or tissue-stimulating proteins to combat bacterial infection.
What is the Procedure of Gum Surgery?
While gum surgery in Jaipur is a relatively advanced procedure, it is done in small, easy steps that cause nominal to zero pain. Here are the basic steps of gum surgery:
- Step 1: The patient is injected with a local anaesthetic to numb the gums.
- Step 2: Sterile equipment is used to make small incisions on the gum line.
- Step 3: The gums are folded away from the teeth.
- Step 4: The dentist removes plaque or any tartar.
- Step 5: After the deep cleaning, procedures like gum reshaping are done.
- Step 6: After the surgery is completed, the gums are stitched back into place.
- Step 7: The stitches are removed a week to ten days later.
What are the Things to Know Before You Get a Gum Surgery?
Gum surgery might be a new treatment option for many. Thus, here are things to know before you get a gum surgery in Jaipur:
- 1. Signs to Get a Gum Surgery
Look out for the signs to get gum surgery before it is too late and the bacterial infection causes pain and discomfort. Common signs include swollen gums with redness and bleeding, as well as mobile teeth.
- 2. Gum Surgery Procedure
Usually, gum surgery is painless throughout. The only discomfort the patient may feel is from the anaesthesia injection required before the surgery.
- 3. Success Rates
The success rates for gum surgeries are very high in the dental domain. However, to maximise the benefits of the surgery, it is important to follow your dentist’s instructions.
- 4. Aftercare
After the surgery is done and you are allowed to go home, you would be advised not to touch the affected area with your fingers or your tongue. If you see swelling, you may use a nice pack and eat softer food or even beverages.
- 5. Different Options
There are different types of dental procedures to cure gum issues. Some of them have gums folded away from the teeth while others have more cosmetic procedures. To get the best-suited treatment, have a thorough discussion with your dentist.
- 6. Benefits of Gum Surgery
Gum surgery in Jaipur offers patients many benefits, including stabilising the gum and the teeth and keeping them in good shape without further decay. It also helps resolve tooth sensitivity and enhances dental aesthetics.
Transform Your Smile with Expert Dental Care!
Let’s Request a Schedule For Consultation
Book AppointmentWhat to Expect During the Gum Surgery?
During periodontal surgery in Jaipur, most patients remain unaware of the procedure, which can easily add up to anxiety. Hence, here are the things to an expert during a gum disease treatment in Jaipur:
1. Anesthetic Injection
Before the surgery starts, your dentist will give you local anaesthesia to numb the gums and your teeth in the affected area. The options for sedation dentistry vary from dentist to dentist, so it is wise to ask about it beforehand.
2. Prepare the Area
The dentist checks the affected area, and after you feel comfortable, a small cut or incision is made to create a flap in your gums. Your teeth roots are cleaned, too.
3. Gum Grafts
Then, in a gum graft surgery, grafts are harvested from the tissue from the roof of your mouth. This is done by creating an incision on the tissue and removing a small piece of the inner tissue.
4. Place the Gums
The gum graft is placed on the target site and your exposed teeth roots in case of recessions. This is carefully placed to fill the space perfectly without affecting the inner tissue.
5. Add Sutures
Then, the surgeon adds sutures or stitches to the gum tissue to keep it in place. These stitches stay for about the next one week to ten days and will require removal in the next visit to your dentist.
6. Duration of the Surgery
The surgery lasts around two hours or more. It is most commonly done in two visits, with the first being an assessment while the scheduled surgery takes place during the follow-up visit in the follow-up visit.
How Long Does Gum Surgery Last?
The duration of gum surgery depends on multiple factors, including the number of teeth being treated and the type of surgery. If only one tooth needs attention and care, it could take an hour, while more teeth may mean more time.
The entire gum surgery process is completed in one sitting. However, the aftercare may take a week or more. Patients are not allowed to eat hard food for the next few days and are even prohibited from touching the affected area.
What are the Benefits of Gum Surgery?
Here are the various benefits of gum surgery that patients might not be aware of:
1. Reduces Gum Disease Severity
The gum diseases, once treated, do not jump back in that easily. In addition, having the treatment in time reduces the chances of severe circumstances such as tooth loss or heavy dental pain.
2. Decreases Sensitivity
Teeth sensitivity is common when the gums are affected by gum decay or disease. Treating the gums as soon as possible keeps the dental area clean and clear and also avoids tooth sensitivity.
3. Improves Smile Appearance
Certain gum procedures are done for aesthetic reasons, wherein the patient gets teeth and gum enhancement. This improves the smile appearance of the patient as well.
4. Reduces Risk of Cavities
With a professional gum disease treatment, the risk of cavities also decreases. This is because the exposed teeth attract more infection and cavity-causing bacteria, so with proper treatment, the risks are reduced.
5. Reduces Bacterial Growth
Gum surgery in Jaipur helps keep bacterial growth in the region and maintains oral hygiene for the individual. Getting gums treated also keeps a lot of diseases at bay.
6. Increases Convenience
Gum diseases are often painful and increase sensitivity in the region. In addition, they can also lead to mobile teeth and painful eating experiences. Getting surgery fixes all these issues.
What Happens After Gum Surgery?
After the gum surgery is completed, you will still have gauze and dressing in your affected area. The gauze is usually allowed to be removed after half an hour with the dentist’s permission. The dressing, however, will fall off on its own after a few days. If it does not, the dentist may remove it during the follow-up checkup.
Your surgeon will then check your vitals to prepare for your discharge. If the tests conclude it is safe for you to leave for home, then you will be allowed to go with a trusted member of your family or a friend. That is done to ensure that the sedatives given to you during the procedure do not pose a risk while getting home. Additionally, a list of post-surgical guidelines will be shared for you to follow for faster recovery.
What is the Recovery Time for Gum Surgery?
Recovery from gum surgery may take one week or more, depending on the type of surgery and the number of gum grafts performed. Until the full recovery happens, a routine checkup with your dentist is sure to follow. During this entire period, there are certain things you can expect. Such as:
- The First Day
After the gum surgery in Jaipur, there will be some initial redness, swelling, and even bleeding around the affected area. Your dentist will give you medications to manage these side effects. In this phase, rest and softer and colder foods such as pudding and yoghurt are suggested. Brushing directly on the area is also advised against.
- The First Week
The bleeding should stop in the first two days,, and the swelling should subside in three to four days. Bruising in the area could also develop. Softer foods, such as eggs and pasta, are good intake options for this period. In addition, brushing directly over the target area should be avoided.
- The Second Week
During this time, the bruising should top, and the swelling should also be gone. When the discomfort comes down, you can ask your surgeon or dentist to reduce your medications for pain and other side effects. With a green light from your dentist, you may start brushing in the operated area, too.
How to Take Care of Yourself Post-Gum Surgery?
Here are the most effective tips to take care of yourself post-gum surgery:
- Eating Cold and Soft Food
After your surgery, you may feel a little sensitive in the operated area. It is usually advised that you eat cold, soft foods like pudding and smoothies and avoid hot foods and drinks.
- Avoid Brushing in the Area
Until your dentist allows you to, avoid brushing the area or even using floss around it. Doing so could damage the sutures and cause you extra pain.
- Rest for Recovery
Resting is crucial post-surgery. This not only boosts the process of recovery but also ensures that you do not harm the place or create more discomfort through continuous actions.
- Routine Check-ups
Always be sure to visit your dentist as per the routine check-up dates to keep track of a speedy recovery. Your medications may be decreased, increased or even changed during these visits, so it is essential to follow through.
- Use Ice Pack for Swelling
If you notice swelling in the region in the initial days, know that it is a common symptom after surgery, and there is nothing to worry about. You may use an ice pack for the swelling and discomfort and hold it against your face.
- Avoid Touching the Area
After surgery, strictly avoid touching the area with your fingers or even tongue to avoid infections and unwanted ruptures. Contact with the area should be avoided for the first few days before the dentist approves to brush around it.
What are the Limitations of Gum Surgery?
There are certain limitations of gum surgery that might affect the patient’s decision. These limitations are:
- 1. Possible Rejection of Gum Graft
The gum graft planted over your teeth after the surgery could,, in some but few cases,, be rejected by your body. In that case, a surgeon would have to remove it.
- 2. Excessive Bleeding and Discomfort
The initial days after the surgery may be accompanied by bleeding, swelling, redness, and discomfort in the mouth, which can make eating anything hard and painful.
- 3. Sensitivity
Your teeth and gums may become extremely sensitive post-surgery, causing discomfort. Your surgeon may prescribe certain medications for the same to curb the problem.
- 4. Recurrence of Gum Recession
Gum recession, wherein the gum line pulls away from the teeth, may occur again after the surgery if the surgeries are not successful or any other complication persists
- 5. Infection
Although rare, if the clinic where the surgery is performed does not use fully sterile materials and has unsanitary practices, you may develop an infection in your mouth post-surgery.
- 6. Tedious Aftercare
After the surgery is over and you are allowed to go home, a list of guidelines to follow is given to you. Some common things included are not brushing in the area, eating soft and cold foods and many more, which can be tedious for many.
Cost of Getting Gum Reshaping Surgery in Jaipur
The cost of gum surgery in Jaipur might not be common knowledge. Hence, here are the details:
1. Type of Gum Disease
The type of gum disease you have can determine the type of surgery you undergo, which inherently contributes to the variation in the final price of the treatment.
2. Number of Teeth
Usually, the gum grafting techniques are performed separately for each tooth. So, the more teeth there are, the higher the price for the entire surgical procedure.
3. Dentist’s Experience
The dentist’s experience matters a lot since it is the expertise and experience that allow a patient to put trust in the hands of the dentist. Hence, surgeons with more experience charge more as well.
4. Location of the Clinic
The location of the clinic also determines the rates for the procedures. In most metropolitan cities, the cost of surgery is usually high. However, in Jaipur, especially at Dr. Renu’s Clinic, patients are given affordable options.
Myth & Fact
What are the Common Myths About Gum Surgery?
Here are the common myths about gum surgery that are not to be followed:
Myth : Gum Disease is Rare
Fact: Gum disease is more prevalent than most people understand. This is why getting yourself dental checkups on a regular basis is important for good oral health.
Myth : Family History does not Matter
Fact: Gum disease is hereditary and can be genetically passed down from parents to children. This is why it is important to keep track of your family history and get yourself routinely checked up.
Myth : Bleeding While Brushing is Normal
Fact: While some people sometimes see bleeding while brushing, it is surely not a normal scenario. This could be one of the early signs of gum disease and should be checked.
Myth : Gum Disease Only Affects the Mouth
Fact: Gum disease not only affects the gums and the teeth but can also spread to other parts of your body. Left untreated, gum disease may travel through your bloodstream and even put your major organs, like your heart and brain, at risk.
Myth : Gum Damage is Irreversible
Fact: Gum damage is not permanent with the modern mechanics of medicine today. With the advancements, various surgical procedures can be performed to cure gum damage fully.
Myth : Gum Disease can be Cured with Brushing
Fact: While maintaining good oral hygiene helps in avoiding gum diseases in the future, if you already have one prevailing in your mouth, brushing alone cannot sort it out. You will need to see a dentist.
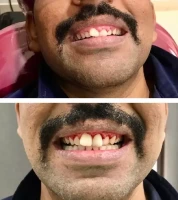
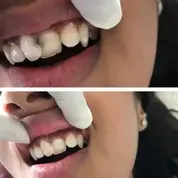
See the Transformation
Remarkable Results with Dr. Renu Dental
See real patient transformations with personalized care. Explore stunning Before & After results at Dr. Renu Dental.
Testimonial (Google Reviews)
Patient Feedback on Google
Here is what our happy patients say on Google about Dr. Renu Dental & Multi Speciality services their visit experience and the results of offered treatments.
Vipin Khandelwal
I had an excellent experience at Dr. Renu Dental Clinic. The staff is incredibly friendly and professional, creating a welcoming and comfortable environment. Dr. Renu's expertise and gentle approach made the treatment smooth and pain-free. They take the time to explain procedures and answer questions, which is truly reassuring. Highly recommend this clinic for anyone seeking quality dental care!
Anshul Kayath
It was really a good experience at Dr. Renu's dental clinic. She treated our daughter's tooth cavity and pulpotomy done by her was painless. Best dental clinic in the area.
V.K h.k
I visited Dr. Renu Dental Clinic for a teeth whitening and smile makeover and couldn’t be happier with the results. Dr. Renu is the best cosmetic dentist in Jaipur, and her attention to detail is impeccable. My teeth are now brighter, and my smile looks better than ever. I highly recommend Dr. Renu for cosmetic dentistry services.
Jyoti
I recently had a root canal procedure and capping of the tooth done at Dr Renu's dental clinic, and I couldn’t be more pleased with the experience. Dr. Renu and her entire staff were exceptional. From the moment I walked in, I was greeted with warmth and professionalism. The procedure was explained thoroughly, and Dr. Renu ensured I was comfortable throughout. The entire team demonstrated great expertise and care, making a potentially stressful experience quite pleasant. The follow-up care has been impeccable, and I’m delighted with the results. I highly recommend Dr.Renu and her team for anyone seeking top-notch dental care."
FAQs
Everything You Need to Know
At our clinic, patient satisfaction and trust are our top priorities. Dr. Renu Chaudhary.
Periodontal surgery is a dental procedure used to treat advanced gum disease, remove infected tissue, and restore gum health. It is recommended when non-surgical treatments are not effective in controlling gum infections. Dr. Renu Dental Clinic in Jaipur offers advanced gum disease treatment to prevent further oral health complications.
Laser gum surgery is a minimally invasive procedure that reduces pain, bleeding, and recovery time. It effectively treats gum infections and reshapes the gums for a healthier smile. At Dr. Renu Dental Clinic, we use advanced laser technology to ensure precision and comfort during the procedure.
The cost of Gum Reshaping Surgery in Jaipur depends on the severity of the condition, the type of procedure required, and the expertise of the dentist. Dr. Renu Dental Clinic provides affordable gum surgery options, ensuring high-quality treatment at a reasonable cost.
Gum flap surgery is a technique where the gums are lifted to clean deep pockets of infection before being repositioned. It is commonly performed for patients with severe periodontal disease. Our gum surgery specialists in Jaipur ensure a painless and effective treatment process.
Gum surgery is not painful, and you can have a comfortable experience during the procedure. The only part of pain is when the anaesthesia is inserted into the gum tissue through a needle.
Gum surgery is a good idea for your condition if your dentist suggests it after evaluating your oral health. Certain gum diseases can only be prevented through this method.
Gum surgery is typically considered a major surgery since it includes treating gums, teeth and mouth with surgical processes such as incisions and sutures, which have to be performed meticulously.
Gum surgery can start healing in the first two weeks and take upto six weeks to fully heal. The graft would become firmer and more comfortable to move your mouth with time.
Gum surgery is a relatively safe surgery and very effective in treating gum diseases and other related issues without many complications.
Getting the gum stitches does not hurt due to the anaesthesia. However, they may later cause a bit of discomfort and uneasiness for the next few days after surgery.
For the first few days after the surgery, avoiding eating hard or hot foods in the part of the mouth with stitches is a good idea and is recommended.
Gum anaesthesia needles are less sharp than the other ones. Hence, they need to be pushed into the gum tissue a little less gently. This could cause a bit of pain initially.
Yes, gum reshaping helps enhance your smile by correcting uneven gum lines and excessive gum tissue. Our cosmetic gum surgery experts in Jaipur at Dr. Renu Dental Clinic use precise techniques to create a balanced and aesthetically pleasing smile.
Gum surgery can be performed at both dental clinics and hospitals in Jaipur. Dr. Renu Dental Clinic specializes in advanced gum treatments, offering advance facilities for safe and effective procedures.











 Facebook
Facebook
 Instagram
Instagram